

The client sends a synchronization request, the server sends back an acknowledgment, and the client returns a synchronization acknowledgment in response.Ĭomparatively, UDP is a connectionless protocol. The connection is established via a three-way handshake. The client must first connect with the server and then send or receive data. A passive open server listens for any client trying to connect with it. Since TCP is a connection-oriented protocol, it relies on a server in a passive open state. TCP is connection-oriented while UDP is connectionless Key Differences Between TCP and UDP for Organizations 1. Transmission control protocol differs from user datagram protocol in the following ways: See More: Top 10 Network Traffic Analysis Tools in 2022 TCP vs. Let us now look at the critical differences between TCP and UDP. There is a possibility that you may lose some data.It is used to send a large number of packets at a time.There will be fewer delays in data transmission.It adapts to bandwidth-intensive applications that tolerate a loss of packets.However, it is preferred mainly for real-time applications like broadcasting or multitasking network traffic. The UDP protocol is not suitable for sending electronic mail, viewing a web page, or downloading a file. In most cases, UDP is faster than TCP because it does not assure delivery of the packets as TCP does. It is commonly referred to as the “fire-and-forget” protocol because it is not concerned about whether or not the client receives the data. In this case, “connectionless” refers to the fact that no connection is established before communication occurs.įurthermore, it does not ensure the delivery of the data packets from the server. What is distinctive about UDP is that it is not connection-based. UDP enables continuous data transmission (i.e., response) without acknowledging or confirming the connectionĪs with TCP, its purpose is to send and receive messages, so its functioning is similar to the transmission control protocol. User datagram protocol (UDP) is a message-oriented communication protocol that allows computing devices and applications to send data via a network without verifying its delivery, which is best suited to real-time communication and broadcast systems.
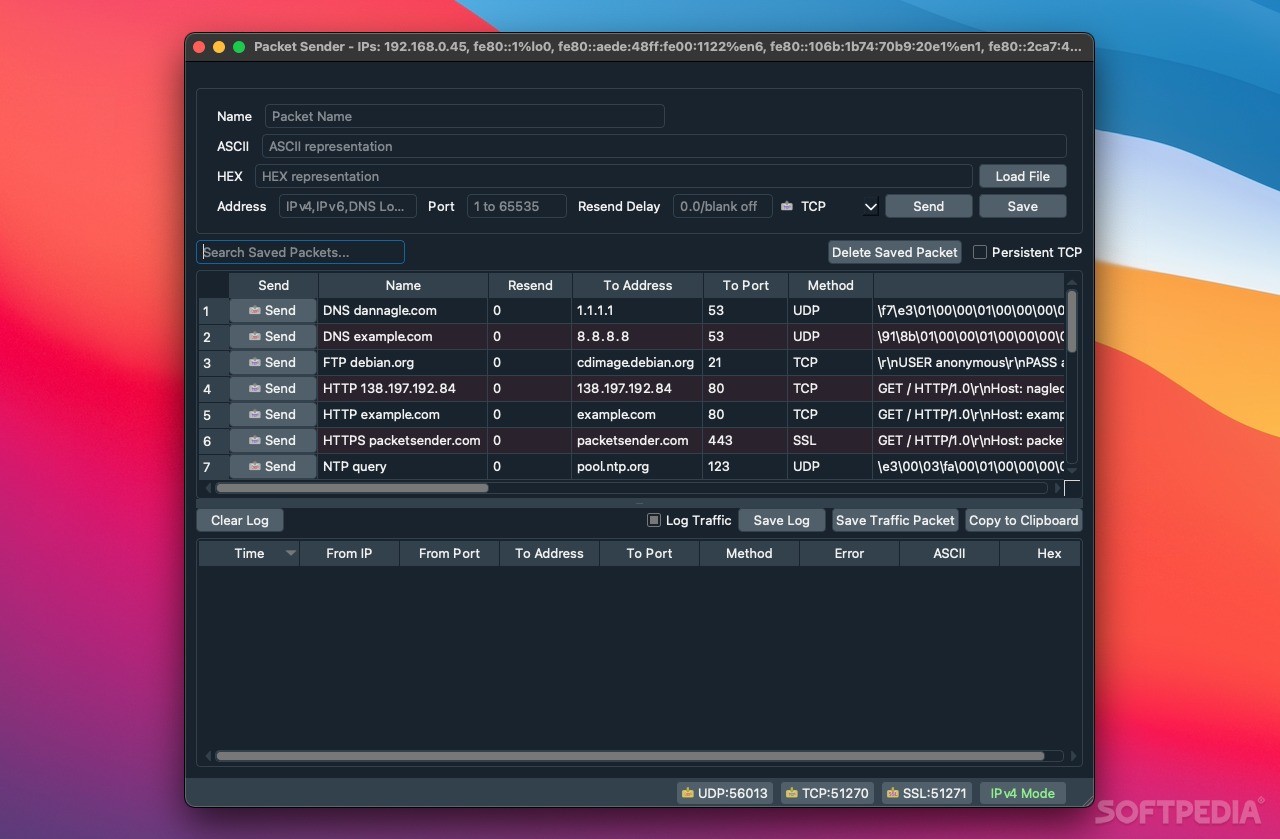
See More: What Is Network Traffic Analysis? Definition, Importance, Implementation, and Best Practices What Is UDP (User Datagram Protocol)? Most online applications use the user datagram protocol (UDP) in conjunction with TCP to work around this issue. This means it will consume significantly more of the bandwidth available on your system. However, while TCP is an instinctively reliable protocol, these feedback mechanisms also result in a more significant overhead size. It uses a three-way handshake to check for data transmission errors.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
